Thoughts on Savings (part 1 of 2)
Mish Moved to MishTalk.Com Click to Visit.
Following is part one in a two part discussion about savings. This part will take a look at what savings are, some charts and other supporting evidence of the unsustainable nature of a US savings rate that has now gone negative. Part two will take a look at Ben Bernanke's viewpoint that there is a glut of savings and the problem is not that the US is spending too little but the rest of the world is not consuming enough. Note: Ben Bernanke is Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisors and possibly next in line to replace Greenspan. Part two will also take a look at the growing national debt, the impact of Katrina, and offer some final comments of the cash flow of consumers. Be sure and stay tuned. Here goes with part one:
Someone recently told me he was saving by contributing to his 401K.
Another person told me he was saving by paying off his home mortgage quicker.
Both of those may be wise decisions but are they savings?
In the strictest definition, savings are that part of your production that is in excess of your consumption. Money is merely a means of channeling, or storing your saved production. Once you've exchanged your real savings for money and go on to invest, you have replaced your savings with investment, while transferring the claim to your savings to someone else.
Under that definition it is clear that paying down one's house mortgage or paying off credit card debts or investing in the stock market is simply not saving. That does not imply these are bad ideas, it just means they are not savings.
Frank Shostak discusses this concept in Have We Saved Enough? Let's take a look:
If a baker produces ten loaves of bread and consumes one loaf his saving is nine loaves of bread. In other words, saving is the baker’s real income (his production of bread) minus the amount of bread that the baker consumed. The baker’s saving now permits him to secure other goods and services.If I quoted everything of merit in that article I would be reproducing it in its entirety. The concept is important so I suggest it is a worthwhile read. Before continuing on, let's quickly point out that expansion of money supply, whether or not that money ends up in "savings accounts" is not savings either. That concept can easily be proven by adding a extra zero to everyone's paycheck and of course to the cost of goods as well. Savings have not increased, only the denomination on money has. When it comes to home prices, what good does it do you if your home has doubled in price when a replacement home will have doubled in price as well? Of course this does not even delve into the very real possibility that asset prices just might drop.
For instance, the baker can now exchange his saved bread for a pair of shoes with a shoemaker. Observe that the baker’s saving is his realmeans of payment—he pays for the shoes with the saved bread. Likewise, the shoemaker pays for the nine loaves of bread with the shoes that are his real saving.
The introduction of money doesn’t alter what we have so far said. When a baker sells his bread for money to a shoemaker, he has supplied the shoemaker with his saved unconsumed bread. The supplied bread sustains the shoemaker and allows him to continue making shoes. Note that the money received by the baker is fully backed up by his unconsumed production of bread.
Money enables the goods of one specialist to be exchanged for the goods of another specialist. In short, by means of money people can channel real savings, which in turn permits the widening of the process of real wealth generation.
Now what about the case where money is used to buy unprocessed material—is the unprocessed material real saving? The answer is no. The raw material must be processed and then converted into a piece of equipment, which in turn can be employed in the production of final goods and services that are ready for human consumption. In this sense the buyer of unprocessed material transfers his claims on real savings to the seller of material in return for the prospect that the transformed material some time in the future will generate benefits far in excess the cost incurred.
Stephen Roach discussed savings on September 9th in an article entitled The Shoestring Economy . This is one of his better articles as of late and following are the highlights:
Never in modern history has the world’s leading economic power tried to do so much with so little. A saving-short US economy has long pushed the envelope in drawing on foreign capital to subsidize excess consumption. But now Washington is upping the ante as it opens the fiscal spigot to cope with post-Katrina reconstruction at the same time it is funding the ongoing war in Iraq. Could this be a tipping point for America’s shoestring economy?According to the US bureau of economic analysis for the month of July, personal income increased $29.3 billion, or 0.3 percent, and disposable personal income (DPI) increased $27.2 billion, or 0.3 percent. Personal consumption expenditures (PCE) increased $85.7 billion, or 1.0 percent. In June, personal income increased $54.7 billion, or 0.5 percent, DPI increased $45.9 billion, or 0.5 percent, and PCE increased $88.0 billion, or 1.0 percent, based on revised estimates.
For any economy, saving is emblematic of the willingness to defer current consumption in order to invest in the future. America’s problem is that it no longer saves. Its net national saving rate -- the combined saving of individuals, businesses, and the government sector (all adjusted for depreciation) -- has fallen to a record low of only 1.5% of GNP since early 2002. By contrast, this same national saving rate averaged 7.5% over the 40-year period, 1960 to 2000. Unwilling to cut back on investment, a saving-short US economy has become increasingly dependent on surplus foreign saving in order to grow.
Asset-dependent consumers were running a negative personal saving rate to the tune of -0.6% of disposable personal income in July 2005. Not since the Great Depression of the early 1930s have US households been stretched that far. Yet, today, few seem worried about this development. Conventional wisdom has it that “rational” consumers have uncovered new and permanent sources of saving in the form of rapid asset appreciation -- first equities and now homes. .... The American consumer is on the leading edge of the shoestring economy.
The government sector is in a similar position. So far, the Bush Administration has hit Congress with $62 billion in supplemental spending requests in the immediate aftermath of Katrina. The risk is that these disaster-relief appropriations are only a down-payment on the final tab, which eventually will span the gamut -- from infrastructure repair and reconstruction of housing and commercial areas to massive environmental clean-up efforts. In the politically-charged post-Katrina environment, any semblance of fiscal discipline has vanished into thin air. Next year’s federal budget deficit is currently projected at -2.4% of GDP; a conservative estimate of a post-Katrina budget could easily push that figure into the -3.25% to -3.5% range -- virtually identical to peak cyclical shortfalls hit in 2003-04.
One of two things has to happen -- either the US attempts to maintain its current lifestyle and places a greater claim on surplus saving elsewhere in the world or there is a consolidation of discretionary spending by American households and businesses, alike.
The macro conclusions are inescapable: A saving-short US economy that runs a massive current account deficit is effectively living beyond its means. It not only relies on foreign saving to fund domestic growth, but it also lacks the capacity to invest in public goods that may be needed to safeguard its future. Lacking in domestic saving, the shoestring economy is also biased toward chronic under-investment in infrastructure -- leaving itself vulnerable to “breakage.” Whether that breakage comes from within (i.e., Katrina) or from the outside (i.e., terrorism), the shoestring economy runs the risk of being unprepared to ward off such blows in a fragile and dangerous world. An energy shock exacerbates the imbalances that produce such vulnerability. This draws into serious question the resilience that financial markets now seem to be banking on.
In plain English, disposable income went up $27.2 billion (.3%) but spending went up $88 billion (1%). Here it is in chart form:
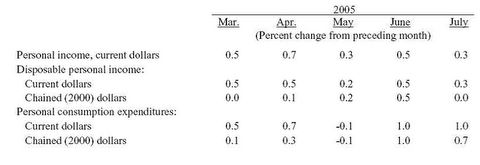
Here are the interesting highlights
- Private wage and salary disbursements increased $29.4 billion in July, compared with an increase of $17.9 billion in June.
- Personal outlays -- PCE, personal interest payments, and personal current transfer payments increased $86.8 billion in July, compared with an increase of $92.8 billion in June. PCE increased $85.7 billion, compared with an increase of $88.0 billion.
- Proprietors' income decreased $3.5 billion in July, in contrast to an increase of $14.7 billion in June.
- Farm proprietors' income decreased $0.5 billion, compared with a decrease of $0.8 billion.
- Nonfarm proprietors' income decreased $3.0 billion, in contrast to an increase of $15.5 billion.
- Rental income of persons decreased $3.3 billion in July, compared with a decrease of $4.3 billion in June.
- Personal income receipts on assets (personal interest income plus personal dividend
- income) increased $7.8 billion, compared with an increase of $18.0 billion. Personal current transfer receipts decreased $4.2 billion, in contrast to an increase of $5.6 billion.
- Contributions for government social insurance -- a subtraction in calculating personal income increased $3.6 billion in July, compared with an increase of $2.1 billion in June.
Personal saving , disposable personal income less personal outlays was a negative $58.8 billion in July, in contrast to a positive $0.9 billion in June. Personal saving as a percentage of disposable personal income was a negative 0.6 percent in July, compared with 0 percent in June.
Negative personal saving reflects personal outlays that exceed disposable personal income. Saving from current income may be near zero or negative when outlays are financed by borrowing (including borrowing financed through credit cards or home equity loans), by selling investments or other assets, or by using
savings from previous periods.
Not only are we not saving, we are now borrowing simply to support consumption.
On that note Mish is taking telepathic questions. Hmmm questions just came pouring in. Let's address them while the telepathic lines are still open.
Q1) Mish has the US always been a nation of spending fools?
A1) No, as hard as it might be for some to remember, as recently as 1992 the savings rate is the US was as high a 10%. Here is a chart to prove it.

Q2) Mish what does retail spending look like now as compared to historical growth?
A2) It seems as if we are now treating our houses as ATMs since wage growth is not keeping up. I offer this chart as evidence.
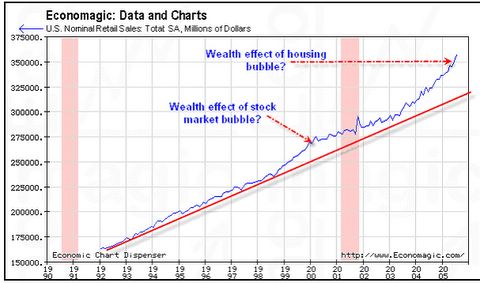
Q3) Mish is there any evidence of consumer stress as a result of all this spending?
A3) Yes indeed there is. We are finally starting to see a big uptick in mortgage defaults and delinquencies. As long as home prices allowed equity extraction everyone was OK. Unfortunately it now seems that appreciation has not kept up with expenditures. I offer the following chart as proof.
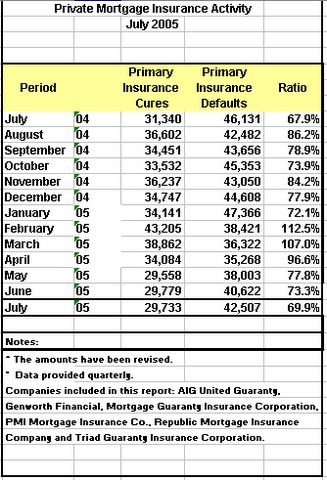
Note that PMI defaults bottomed in April but have ticked up every month since then. Also note that cures (those that were in delinquent but managed to catch up), topped in February and have been declining ever since. This is a clear sign that rising home prices are no longer sustaining consumption at least in some areas. Watch what happens when housing prices take a serious hit in California or Florida. It will not be pretty.
Mike Shedlock / Mish
http://globaleconomicanalysis.blogspot.com/



